Spanish Colonisation of the Americas
Unit Outline:
Students will explore the main features of the Aztec culture prior to colonisation. They will also learn about the nature and impact of colonisation and contact on indigenous peoples.
Key Concepts:
This topic builds upon prior learning of Aboriginal and non-Aboriginal contact history in Stages 1–3. The nature of colonisation and its impact on indigenous peoples. Also links to the topic ‘Changing Rights and Freedoms’, covered in Stage 5 History. Students will develop an understanding of the impact of colonisation upon another indigenous people.
Targeted Outcomes:
- Colonisation - what is it?
- Why did Europeans want to colonise?
- Outline impacts on indigenous peoples
Students will explore the main features of the Aztec culture prior to colonisation. They will also learn about the nature and impact of colonisation and contact on indigenous peoples.
Key Concepts:
- That we learn from the past, and apply this learning to their interactions with people today
- That we engage with a range of sources and further their ability to conduct historical research
- Students will develop an understanding of the impact of colonisation upon indigenous people across the world.
- The ability to analyse information for perspective and content is a key requirement for informed citizenship.
This topic builds upon prior learning of Aboriginal and non-Aboriginal contact history in Stages 1–3. The nature of colonisation and its impact on indigenous peoples. Also links to the topic ‘Changing Rights and Freedoms’, covered in Stage 5 History. Students will develop an understanding of the impact of colonisation upon another indigenous people.
Targeted Outcomes:
- HT4-2: describes major periods of historical time and sequences events, people and societies from the past
- HT4-3: describes and assesses the motives and actions of past individuals and groups in the context of past societies
- HT4-4: describes and explains the causes and effects of events and developments of past societies over time
- HT4-6: uses evidence from sources to support historical narratives and explanations
- HT4-10: selects and uses appropriate oral, written, visual and digital forms to communicate about the past
- Colonisation - what is it?
- Why did Europeans want to colonise?
- Outline impacts on indigenous peoples
Definition of Colonisation
Colonisation is the forming of a settlement or colony by a group of people who seek to take control of territories or countries. It usually involves large-scale immigration of people to a 'new' location and the expansion of their civilisation and culture into this area. Colonisation may involve dominating the original inhabitants of the area, known as the indigenous population.
Colonisation is the forming of a settlement or colony by a group of people who seek to take control of territories or countries. It usually involves large-scale immigration of people to a 'new' location and the expansion of their civilisation and culture into this area. Colonisation may involve dominating the original inhabitants of the area, known as the indigenous population.
Introduction
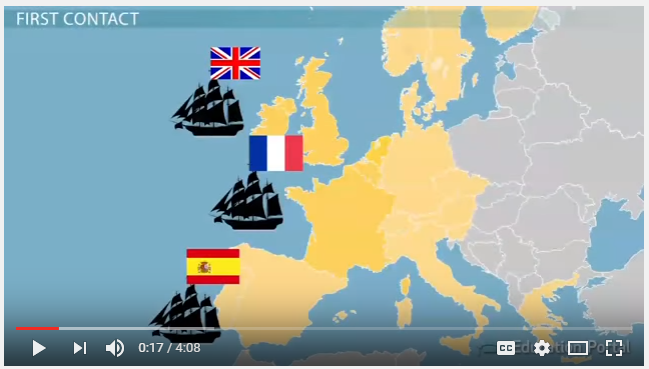
In the fifteenth century (1400s), sea-going explorers from Europe and Asia began to sail beyond what was then the known world. Between 1405 and 1433 Admiral Zheng He sailed all the way from China to Africa, coming into contact with many civilisations en route. After 1419 several European nations began to explore, the Portuguese sailing south down the west coast of Africa, the Spanish crossing the Atlantic towards the Caribbean and South America, and the British and French exploring North America. Unlike Admiral Zheng He, the Europeans explored with the intention of colonising the places they found. They conquered the new lands and exploited them for all the gold, silver and wildlife that they could find. For the indigenous people of these lands, contact with the European colonisers was very destructive and little remains of their civilisations. In contrast, for the Europeans colonisation often meant acquiring fame and wealth beyond their wildest dreams.
In the fifteenth century (1400s), sea-going explorers from Europe and Asia began to sail beyond what was then the known world. Between 1405 and 1433 Admiral Zheng He sailed all the way from China to Africa, coming into contact with many civilisations en route. After 1419 several European nations began to explore, the Portuguese sailing south down the west coast of Africa, the Spanish crossing the Atlantic towards the Caribbean and South America, and the British and French exploring North America. Unlike Admiral Zheng He, the Europeans explored with the intention of colonising the places they found. They conquered the new lands and exploited them for all the gold, silver and wildlife that they could find. For the indigenous people of these lands, contact with the European colonisers was very destructive and little remains of their civilisations. In contrast, for the Europeans colonisation often meant acquiring fame and wealth beyond their wildest dreams.
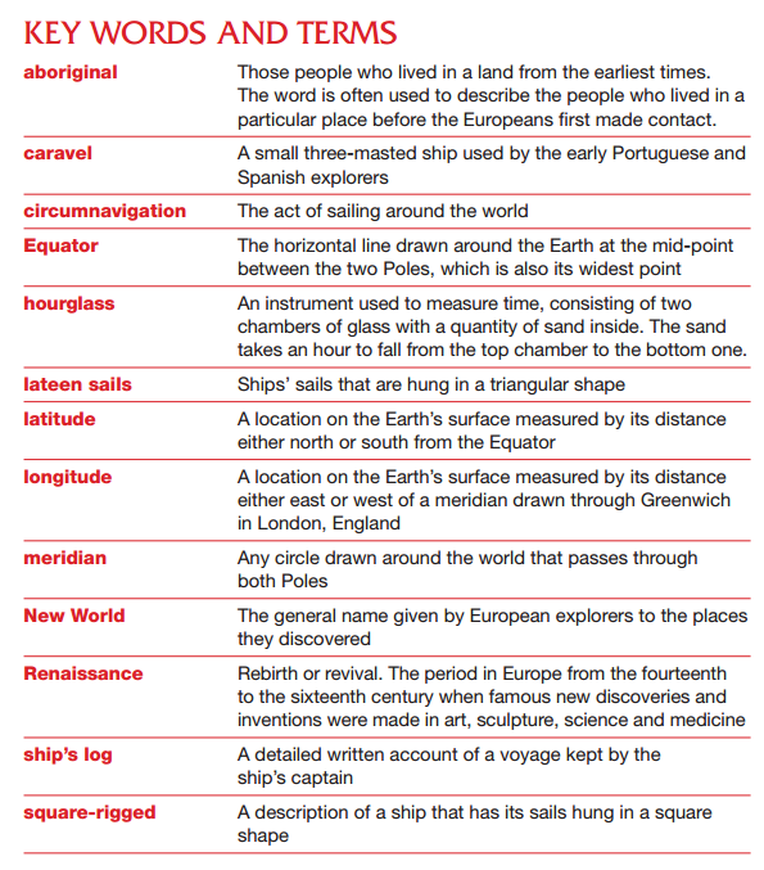
Glossary
| spanish_colonisation_glossary_activity.docx | |
| File Size: | 449 kb |
| File Type: | docx |
Activity
Students construct a mind map after class views videos No. 2 & 3 below
Students construct a mind map after class views videos No. 2 & 3 below
Blank Mind Map worksheet
| spanish_colonisation_mind_map.docx | |
| File Size: | 30 kb |
| File Type: | docx |
Exploration Timeline
Activity
Students construct linear timeline
Students construct linear timeline
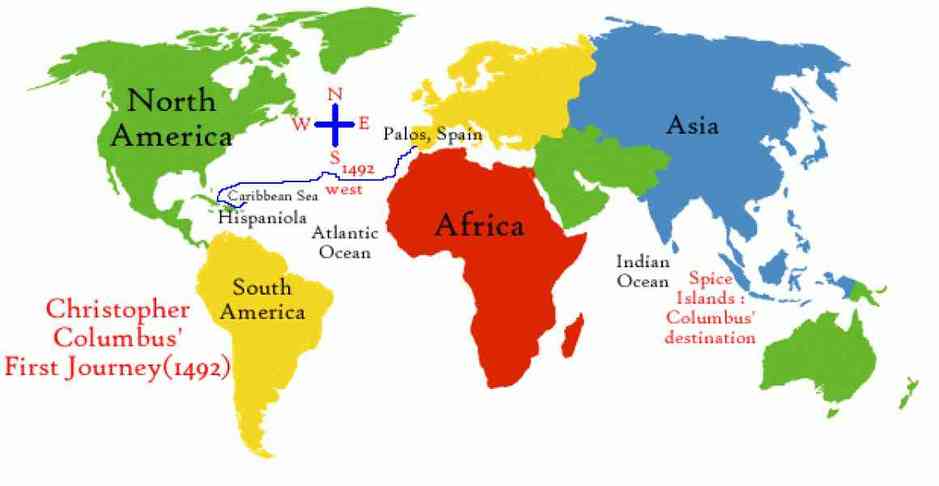
Columbus' Route
Activity
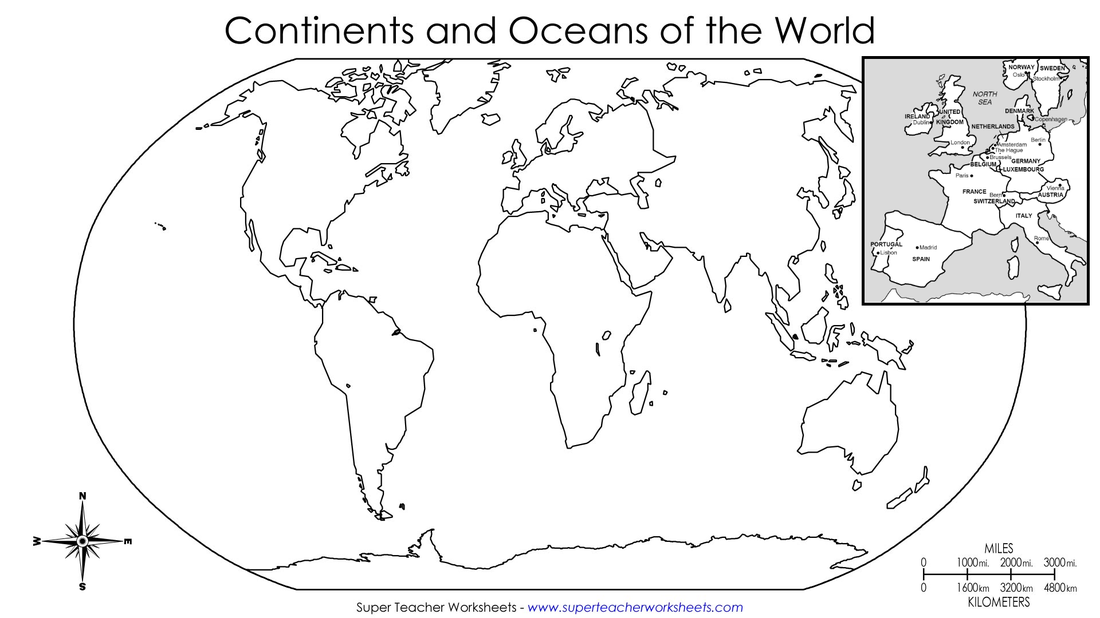
Using the blank World Map below students label:
- Columbus' Route
- Continents: Africa, South America, North America, Central America, Australia, Antarctica, Asia, Europe
- Countries: Spain, India, China, Spice Islands, West Indies
- Oceans: Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, Pacific Ocean
Using the blank World Map below students label:
- Columbus' Route
- Continents: Africa, South America, North America, Central America, Australia, Antarctica, Asia, Europe
- Countries: Spain, India, China, Spice Islands, West Indies
- Oceans: Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, Pacific Ocean
| blank_world_map_with_europe_insert.docx | |
| File Size: | 583 kb |
| File Type: | docx |
Maritime Explorers
| admiral_zheng_he_cloze_passage.docx | |
| File Size: | 17 kb |
| File Type: | docx |
Activity: Class views videos No. 1 & 4 below and constructs an Explorers Mind Map
| blank_explorers_mind_map.docx | |
| File Size: | 21 kb |
| File Type: | docx |
Videos
Watch: 1. Columbus, de Gama, and Zheng He! 15th Century Mariners. Crash Course: World History #21
Watch: 2. Effects of European Colonization: Christopher Columbus and Native Americans
Watch: 3. The Columbian Exchange: Crash Course World History #23
Watch - 4. "Zheng He" - The Great Voyager 1405-1433 AD
Text Book Chapters
Experience World History - Chapter 8 The Age of Exploration
Mason, J., Fielden, P., Burgess, C., Myers, J. (2004). Experience World History. McGraw-Hill, North Ryde.
Mason, J., Fielden, P., Burgess, C., Myers, J. (2004). Experience World History. McGraw-Hill, North Ryde.
| chapter_08.pdf | |
| File Size: | 2259 kb |
| File Type: | |
RetroActive 1 - Contact and Colonisation in North America
| ra1-2e-ch10.pdf | |
| File Size: | 12213 kb |
| File Type: | |
Chapter 9 - God, Gold and Glory: The colonisation of the Americas
Darlington, R., & Greer, V. (2000). A History of people, events and cultures (1st ed.). Port Melbourne, Vic.: Heinemann.
Darlington, R., & Greer, V. (2000). A History of people, events and cultures (1st ed.). Port Melbourne, Vic.: Heinemann.
| spanish_colonisation_of_the_americas.pdf | |
| File Size: | 43451 kb |
| File Type: | |