Introduction to Geography
What is Geography?
Watch: Pause at 2:30
Watch to 1:20
What do Geographers do?
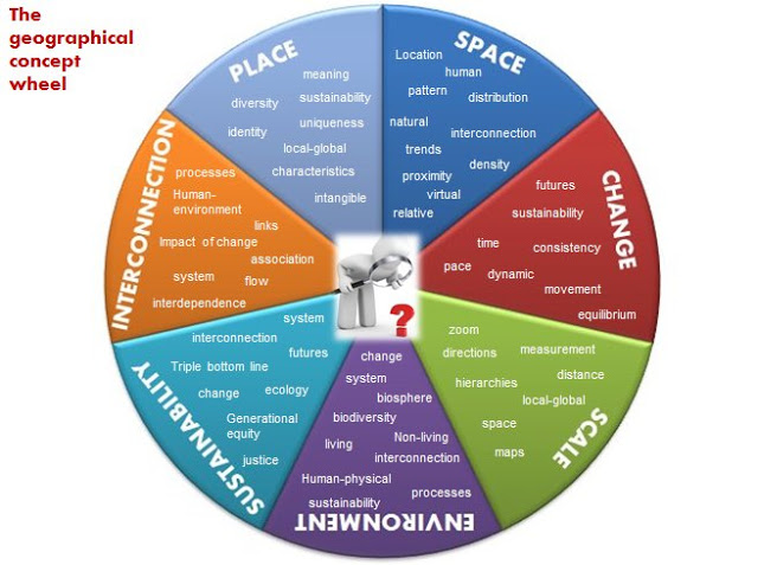
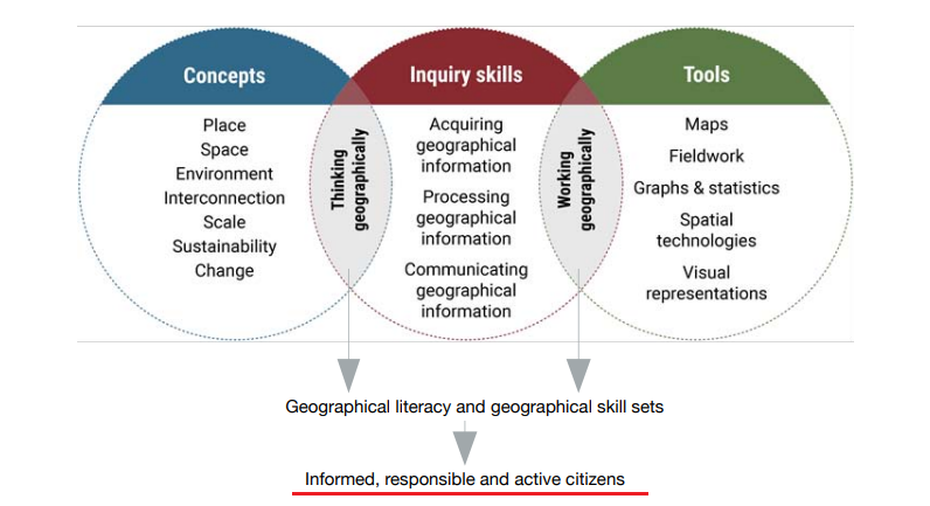
GEOGRAPHICAL CONCEPTS - SPICESS
• Space: the significance of location and spatial distribution, and ways people organise and manage the spaces that we live in eg spatial distribution of landscapes, global water resources and natural hazards; how location influences the ways people organise places.
• Place: the significance of places and what they are like eg factors influencing people’s perceptions of places; the special significance place has to some people; the effect of global trade, transport, information and communication technologies on places across the world.
• Interconnection: no object of geographical study can be viewed in isolation eg how people are affected by the environment with regard to landscapes, climate, natural hazards and the liveability of places; how people affect the environment such as people’s use of water on its quality and availability as a resource.
• Change: explaining geographical phenomena by investigating how they have developed over time eg changes to resources, landscapes and places over time through natural and human geographical processes and events; the effect of management strategies in reducing the impact of natural and human geographical processes.
• Environment: the significance of the environment in human life, and the important interrelationships between humans and the environment eg processes that form and transform landscapes and landforms across the world; the aesthetic, cultural, spiritual and economic value of environments to people; the effect of human activities on natural and human environments.
• Scale: the way that geographical phenomena and problems can be examined at different spatial levels eg management of geographical challenges across a range of scales from local to global; responses and actions undertaken by governments, organisations and individuals; communities operating at local to global scales.
• Sustainability: the capacity of the environment to continue to support our lives and the lives of other living creatures into the future eg pressures on the Earth’s water resources and landscapes; the need to manage environments for a long-term future; sustainable management approaches.
• Space: the significance of location and spatial distribution, and ways people organise and manage the spaces that we live in eg spatial distribution of landscapes, global water resources and natural hazards; how location influences the ways people organise places.
• Place: the significance of places and what they are like eg factors influencing people’s perceptions of places; the special significance place has to some people; the effect of global trade, transport, information and communication technologies on places across the world.
• Interconnection: no object of geographical study can be viewed in isolation eg how people are affected by the environment with regard to landscapes, climate, natural hazards and the liveability of places; how people affect the environment such as people’s use of water on its quality and availability as a resource.
• Change: explaining geographical phenomena by investigating how they have developed over time eg changes to resources, landscapes and places over time through natural and human geographical processes and events; the effect of management strategies in reducing the impact of natural and human geographical processes.
• Environment: the significance of the environment in human life, and the important interrelationships between humans and the environment eg processes that form and transform landscapes and landforms across the world; the aesthetic, cultural, spiritual and economic value of environments to people; the effect of human activities on natural and human environments.
• Scale: the way that geographical phenomena and problems can be examined at different spatial levels eg management of geographical challenges across a range of scales from local to global; responses and actions undertaken by governments, organisations and individuals; communities operating at local to global scales.
• Sustainability: the capacity of the environment to continue to support our lives and the lives of other living creatures into the future eg pressures on the Earth’s water resources and landscapes; the need to manage environments for a long-term future; sustainable management approaches.
GEOGRAPHICAL TOOLS
Examples may include:
Maps – M
• sketch maps, relief maps, political maps, topographic maps, flowline maps, choropleth maps, isoline maps, précis maps, cultural mapping, cartograms, synoptic charts
• maps to identify direction, scale and distance, area and grid references, latitude and longitude, altitude, area, contour lines, gradient, local relief
Fieldwork – F
• observing, measuring, collecting and recording data, developing and conducting surveys and interviews
• fieldwork instruments such as weather instruments, vegetation identification charts, compasses, GPS, GIS
Graphs and statistics – GS
• data tables, pie graphs, column graphs, compound column graphs, line graphs, climate graphs, population profiles, multiple tables and graphs presented on a geographical theme, statistics to find patterns and trends
Spatial technologies – ST
• virtual maps, satellite images, global positioning systems (GPS), geographic information systems (GIS)
Visual representations – VR
• photographs, aerial photographs, illustrations, flow charts, annotated diagrams, multimedia, field sketches, cartoons, web and app tools
Examples may include:
Maps – M
• sketch maps, relief maps, political maps, topographic maps, flowline maps, choropleth maps, isoline maps, précis maps, cultural mapping, cartograms, synoptic charts
• maps to identify direction, scale and distance, area and grid references, latitude and longitude, altitude, area, contour lines, gradient, local relief
Fieldwork – F
• observing, measuring, collecting and recording data, developing and conducting surveys and interviews
• fieldwork instruments such as weather instruments, vegetation identification charts, compasses, GPS, GIS
Graphs and statistics – GS
• data tables, pie graphs, column graphs, compound column graphs, line graphs, climate graphs, population profiles, multiple tables and graphs presented on a geographical theme, statistics to find patterns and trends
Spatial technologies – ST
• virtual maps, satellite images, global positioning systems (GPS), geographic information systems (GIS)
Visual representations – VR
• photographs, aerial photographs, illustrations, flow charts, annotated diagrams, multimedia, field sketches, cartoons, web and app tools
The Earth's Spheres
Watch:
Human Geography
Things made by people are said to be the HUMAN ELEMENTS of environments. It issometimes known as the built environment.
Agricultural - Farms, Gardens
Industrial - Factories
Settlements - Cities, Towns
Economic - Money, Shops
Political - Council, Government
Sociocultural - Theatres, Churches
Things made by people are said to be the HUMAN ELEMENTS of environments. It issometimes known as the built environment.
Agricultural - Farms, Gardens
Industrial - Factories
Settlements - Cities, Towns
Economic - Money, Shops
Political - Council, Government
Sociocultural - Theatres, Churches
Watch: What is human geography?
**Landscapes & Landforms**
Watch: Landforms: Crash Course
| landscapes_and_landforms_.pptx | |
| File Size: | 14447 kb |
| File Type: | pptx |
Student Workbook
| landscapes_and_landforms_student_booklet.docx | |
| File Size: | 5697 kb |
| File Type: | docx |
Plate Tectonics
Watch:
Watch:
Mountain Landscapes
| mountain_landscapes.pptx | |
| File Size: | 15283 kb |
| File Type: | pptx |
Processes That Transform Landscapes
| processes_that_transform_landscapes.pptx | |
| File Size: | 6544 kb |
| File Type: | pptx |
Watch: Weathering and Erosion: Crash Course
Worksheet
Valuing, Managing and Protecting Landscapes & Landforms
.
1. What are the four types of deserts?
2. Where are Subtropical Deserts are found?
3. Where are semi-arid deserts found?
4. Where do coastal deserts form?
5. Where are Polar deserts found?
6. Why are deserts becoming less habitable?
2. Where are Subtropical Deserts are found?
3. Where are semi-arid deserts found?
4. Where do coastal deserts form?
5. Where are Polar deserts found?
6. Why are deserts becoming less habitable?